The piriformis muscle, located deep in the buttocks, plays a crucial role in hip rotation and stabilizing the pelvis. It is essential for maintaining proper posture and movement.
Understanding its function is vital for addressing issues like piriformis syndrome, which often requires targeted exercises to alleviate discomfort and restore mobility, as detailed in various exercise guides.
1.1 Understanding the Role and Function of the Piriformis Muscle
The piriformis muscle is a small, deep muscle in the buttocks that plays a key role in hip rotation and stabilization. It originates from the anterior surface of the sacrum and inserts onto the greater trochanter of the femur. Its primary function is to externally rotate the hip joint and assist in stabilizing the pelvis during walking and running. Proper functioning of the piriformis muscle is essential for maintaining balance, posture, and efficient movement patterns.
Dysfunction or tightness in this muscle can lead to discomfort and mobility issues, emphasizing the importance of targeted exercises to restore its optimal function and prevent related conditions.
1.2 Common Issues Related to the Piriformis Muscle
The piriformis muscle is often associated with issues like piriformis syndrome, where the muscle irritates the sciatic nerve, causing pain and discomfort. Tightness or spasm in the muscle can lead to limited mobility and pain in the buttocks or thighs. Prolonged sitting, repetitive movements, or sudden trauma can exacerbate these issues, making it essential to address them through targeted exercises and therapies to restore proper muscle function and alleviate symptoms.
Additionally, inflammation or strain in the piriformis muscle can contribute to conditions like sciatica and sacroiliac joint dysfunction, further highlighting the importance of maintaining its health.

Symptoms of Piriformis Syndrome
Piriformis syndrome often causes buttock pain, which may radiate along the sciatic nerve. Pain typically worsens with sitting or activities involving hip internal rotation.
2.1 Identifying Pain and Discomfort Associated with Piriformis Syndrome
Pain from piriformis syndrome is typically felt in the buttocks and may extend along the sciatic nerve, causing discomfort in the back of the leg. It often worsens with prolonged sitting, standing, or activities that involve internal hip rotation. The pain is usually unilateral, affecting one side of the body, and can be exacerbated by movements like walking or climbing stairs. Proper identification of these symptoms is crucial for effective treatment and management of the condition, often involving specific exercises to relieve tension and improve mobility.
2.2 How Symptoms Relate to Sciatica and Other Conditions
Piriformis syndrome symptoms often mimic those of sciatica, as the piriformis muscle can compress the sciatic nerve. This can lead to similar pain patterns, including radiating discomfort down the leg. It is crucial to differentiate piriformis syndrome from other conditions like sacroiliac joint dysfunction or gluteal tendinopathy, which may present with overlapping symptoms. Accurate diagnosis ensures targeted treatment, often involving specific exercises to address the root cause of the pain and restore proper muscle function.

Importance of Piriformis Exercises
Piriformis exercises are crucial for alleviating pain, improving muscle balance, and preventing future issues. They strengthen and stretch the muscle, enhancing mobility and reducing discomfort effectively.
3.1 Benefits of Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Stretching enhances flexibility and reduces muscle tightness, while strengthening improves stability and support. Together, they alleviate pain, promote proper posture, and enhance overall mobility.
Regular stretching and strengthening exercises target the piriformis muscle, reducing discomfort and preventing future issues. They improve blood flow, reduce muscle spasms, and support daily activities and athletic performance effectively.
3.2 Role of Exercise in Treating Piriformis Syndrome
Exercise is a cornerstone in managing piriformis syndrome, reducing sciatic nerve irritation and muscle spasms. It improves flexibility, strength, and posture, addressing root causes of discomfort.
Targeted stretches and strengthening routines help restore normal muscle function, alleviate pain, and prevent recurrence, making exercise a highly effective treatment approach for this condition.
Stretching Exercises for Piriformis Muscle
Stretching exercises target the piriformis muscle to improve flexibility and reduce tension. These exercises help alleviate symptoms of piriformis syndrome and enhance overall hip mobility.
4.1 Supine Piriformis Stretch
Lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat. Cross the affected leg over the other thigh. Grasp the unaffected leg and gently pull it toward your chest until a stretch is felt in the buttock. Hold for 20-30 seconds and repeat 2-3 times. This stretch targets the piriformis muscle, helping to relieve tension and improve hip flexibility while reducing discomfort associated with piriformis syndrome.
4.2 Seated Piriformis Stretch
Sit on the floor or a chair with your legs extended. Cross the affected leg over the other thigh, placing your ankle on the opposite knee. Gently lean forward from your hips until a stretch is felt in the buttock. Hold for 20-30 seconds, then repeat on the other side. This stretch helps relieve tension in the piriformis muscle, improving hip mobility and reducing discomfort associated with piriformis syndrome. Avoid bouncing and breathe deeply.
4.3 Piriformis Stretch with Hip Rotation
Sit on the floor with your legs crossed, placing your right ankle on your left knee. Gently press down on your right knee while rotating your hip outward. You should feel a stretch in your buttock. Hold for 20-30 seconds, then switch sides. This stretch combines hip rotation with targeted pressure to release tension in the piriformis muscle, helping to alleviate sciatic nerve irritation and improve hip flexibility. Perform 2-3 repetitions on each side.
Strengthening Exercises for Piriformis Muscle
Strengthening the piriformis muscle enhances hip stability and supports lower back health. Targeted exercises, like glute bridges, help improve muscle activation and reduce the risk of injury or strain.
5.1 Glute Bridges for Piriformis Strengthening
Glute bridges are an effective exercise for strengthening the piriformis muscle. Lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat, then lift your hips toward the ceiling, squeezing your glutes at the top. This movement improves muscle activation and hip stability, essential for preventing piriformis-related issues.
Perform 3 sets of 15 repetitions, gradually increasing as strength improves. Proper form ensures targeting the correct muscles without strain, making it a cornerstone of piriformis strengthening routines.
5.2 Side-Lying Abduction for Piriformis Activation
Side-lying abduction targets the piriformis muscle, enhancing its activation and strength. Lie on one side with legs straight, lift the top leg away, and hold briefly before lowering. This exercise improves hip stability and reduces muscle imbalances. Perform 3 sets of 15 repetitions on each side, focusing on controlled movements to maximize piriformis engagement and overall hip function.
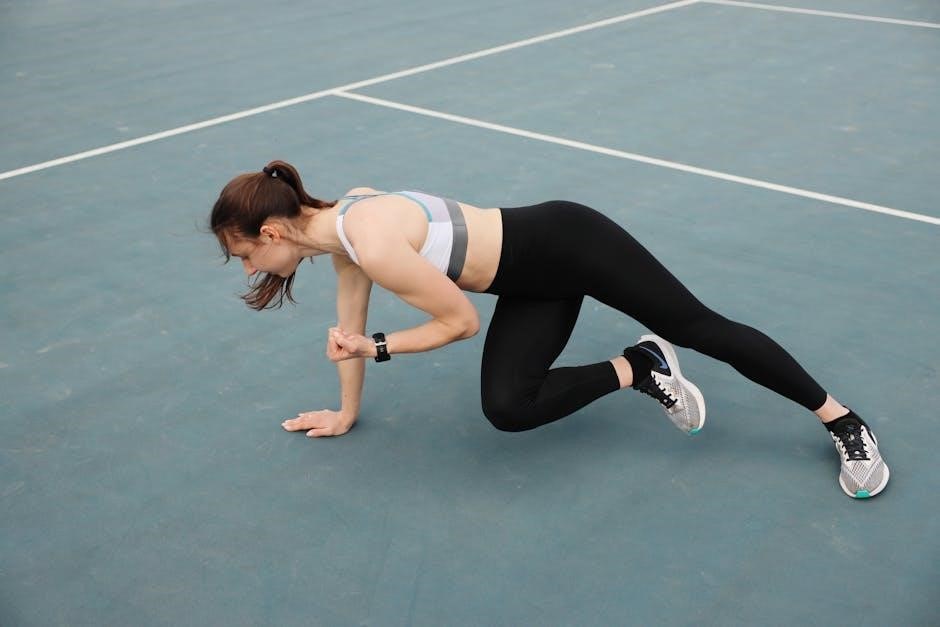
5.3 Bird Dog Exercise for Core and Piriformis Stability
The bird dog exercise strengthens both the core and piriformis muscle. Start on hands and knees, extend one arm and the opposite leg, holding briefly. This improves balance, stability, and coordination while engaging the piriformis. Perform 3 sets of 10 repetitions on each side, ensuring controlled movements to enhance overall stability and reduce injury risk.

Advanced Techniques for Piriformis Exercises
Advanced techniques elevate your exercise routine, incorporating resistance bands for deeper stretches and foam rolling for muscle release, enhancing flexibility and strength effectively.
6.1 Incorporating Resistance Bands for Enhanced Stretching
Resistance bands add tension to stretches, maximizing the effectiveness of piriformis exercises. For the supine piriformis stretch, loop the band around your thigh, gently pulling toward your chest. This enhances the stretch intensity and targets the muscle deeply. Similarly, in seated stretches, wrap the band around your knee, applying controlled resistance to improve flexibility and strength. This advanced technique ensures comprehensive muscle engagement and faster recovery from piriformis-related discomfort.
6.2 Using Foam Rolling for Muscle Release
Foam rolling is an effective technique for releasing tension in the piriformis muscle. By rolling slowly over the buttocks, you can relieve tightness and improve blood flow. This method is particularly useful for self-myofascial release, helping to alleviate muscle soreness and stiffness. Regular foam rolling complements stretching exercises by enhancing muscle recovery and preventing future piriformis-related issues. It’s a simple yet powerful tool for maintaining muscle health and flexibility.
How to Perform Piriformis Exercises Correctly
Proper form is essential for maximizing benefits and preventing injury. Focus on controlled movements, engage your core, and maintain steady breathing to ensure effective execution of exercises.
7.1 Proper Form and Technique for Maximum Benefit
Ensuring proper form during piriformis exercises is crucial for effectiveness and safety. Maintain a neutral spine, engage your core, and focus on slow, controlled movements. Avoid bouncing or forcing stretches beyond a comfortable range. Use props like pillows or blocks if needed to support your body. Breathing deeply can help relax muscles and enhance the stretch. Consistency and attention to detail yield the best results.
Visual Guide to Piriformis Exercises in PDF Format
A downloadable PDF guide provides clear, visual instructions for piriformis exercises, ensuring proper form and maximizing effectiveness. It’s an essential resource for home routines.
8.1 Importance of Visual Aids for Effective Exercise Performance
Visual aids, such as diagrams and images, play a crucial role in ensuring exercises are performed correctly. They provide clear guidance on proper form and technique, reducing the risk of injury and enhancing effectiveness.
In a PDF guide, step-by-step visuals help individuals understand complex movements, making exercises more accessible and achievable, especially for those without professional supervision.
Structuring a Piriformis Exercise Routine
A well-structured piriformis exercise routine should balance stretching, strengthening, and mobility exercises. Start with warm-ups, followed by targeted stretches and strengthening movements, and finish with cool-down stretches.
Consistency and progression are key to achieving optimal results and preventing muscle imbalances. Incorporate exercises that address both the piriformis and surrounding muscles for a comprehensive approach.
9.1 Creating a Balanced Exercise Program
A balanced piriformis exercise program combines stretching, strengthening, and mobility exercises. Begin with a warm-up to prepare the muscles, followed by gentle stretches like the supine piriformis stretch. Incorporate strengthening exercises such as glute bridges and side-lying abductions to build muscle stability. Finish with a cool-down to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension. Consistency and gradual progression are essential for achieving long-term benefits and preventing muscle imbalances.
9.2 Incorporating Warm-Up and Cool-Down Routines
A proper warm-up prepares the piriformis muscle for exercise by increasing blood flow and flexibility, reducing injury risk; Dynamic stretches, such as hip rotations and leg swings, are ideal. After exercising, a cool-down with static stretches, like the seated piriformis stretch, helps relax the muscle and improve recovery. Including these routines ensures a safe and effective workout, promoting long-term muscle health and preventing stiffness or soreness. Consistency is key for optimal results.
Recovery and Prevention Tips
Rest and stretching are crucial for recovery, while consistent exercise and avoiding overuse prevent future piriformis-related issues, ensuring long-term muscle health and optimal functionality.
10.1 Role of Rest and Recovery in Exercise Routine
Rest and recovery are vital for allowing the piriformis muscle to heal and rebuild after exercise. Incorporating rest days ensures muscle fibers repair, reducing inflammation and preventing overuse injuries. Proper recovery, including stretching and low-impact activities, enhances flexibility and strength. Adequate sleep and nutrition also support muscle repair, promoting overall well-being. Neglecting rest can lead to chronic pain and prolonged recovery, emphasizing its importance in a sustainable exercise routine.
10.2 Preventing Future Piriformis-Related Issues
Preventing future piriformis-related issues involves maintaining a consistent exercise routine, focusing on stretches and strengthening exercises. Proper posture, ergonomic adjustments, and avoiding prolonged sitting can reduce muscle strain. Incorporating activities that promote hip flexibility and strength, such as yoga or swimming, also helps. Avoiding repetitive motions that cause internal hip rotation can further minimize the risk of recurrence, ensuring long-term muscle health and functionality.